in cats curled ears result from an allele|In cats, curled ears (Cu) results from an allele that is dominant over : Tuguegarao In cats, curled ears result from an allele ( C u ) that is dominant to an allele (cu) for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant to . Nothing but the highest quality Pinay Leaked Threesome porn on Redtube! This website is for adults only . This website contains age-restricted materials including nudity and explicit depictions of sexual activity. By entering, you affirm that you are at least 18 years of age or the age of majority in the jurisdiction you are accessing the .
in cats curled ears result from an allele,In cats, curled ears result from an allele, Cu, that is dominant over an allele, cu, for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele, G, that is dominant over an allele for gray, g. A gray cat .In cats, curled ears (Cu) results from an allele that is dominant overIn cats, curled ears (Cu) results from an allele that is dominant over an allele for. normal ears (cu). Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that. is dominant .
In cats, curled ears result from an allele $(C u)$ that is dominant over an allele $(c u)$ for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele $(G)$ that is .In cats, curled ears result from an allele ( C u ) that is dominant to an allele (cu) for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant to . In cats, curled ears result from an allele $ (C u)$ that is dominant over an allele $ (c u)$ for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting . Curled ears: F1: 63.5: 45: 1.25: 6: PBX1 3: La Perm: B1: 147.25: 151: 3.75: 26: EPGN, EREG: Curly coat: Ragdoll 1: A1: 82: 89: 7: 40: LAMP1: Multiple: Birman 1: . Cats Have Mobile Outer Ears. Humans have six muscles in our outer ear (pinna). Cats have 32. This anatomy lets them rotate their ears a full 180 degrees! Not .
Find step-by-step Biology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: In cats, curled ears result from an allele $ (\mathrm {Cu})$ that is dominant over an allele $ (\mathrm {cu})$ for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele $ (G)$ that is dominant over an allele for gray $ (g)$.Biology. In cats, curled ears result from an allele, Cu, that is dominant over an allele, cu, for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele, G, that is dominant over an allele for gray, g. A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F1 cats are black and have .
In cats, curled ears results from an allele (Cu) that is dominant over an allele (cu) for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for grey (g). A grey cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the first generation (F1) cats are .
In cats, curled ears result from an allele (Cu) that is dominant over an allele (cu) for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F1 cats are black and have curled .In cats, curled ears result from an allele (Cu) that is dominant over an allele (cu) for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F1 cats are black and have curled .Biology questions and answers. In cats, curled ears (C) result from an allele that is dominant over an allele for normal ears (c). Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears.

In cats, curled ears (C) result from an allele that is dominant over an allele for normal ears (c). Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. What is the genotype and .in cats curled ears result from an allele In cats, curled ears (C) result from an allele that is dominant over an allele for normal ears (c). Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. What is the genotype and .
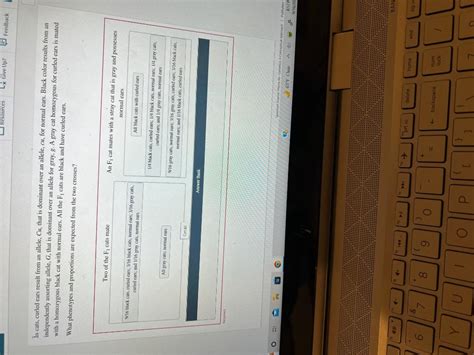
In cats, curled ears result from an allele $(C u)$ that is dominant over an allele $(c u)$ for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele $(G)$ that is dominant over an allele for gray $(g) .$ A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the $\mathrm{F}_{1}$ cats .Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F1 cats are black and have curled ears. a. If two of the F1 cats mate, what phenotypes and proportions are expected in the F2? b.
In cats, curled ears (C) result from an allele that is dominant over an allele for normal ears (C). Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray 9). Two parent cats: A female gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous male cat that is black with normal ears. 1.

In cats, curled ears (Cu) results from an allele that is dominant over an allele for normal ears (cu). Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated to a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F1 cats are black and have curly ears. Step 4: If an F1 cat (CuCugG) mates with a stray cat that is homozygous recessive (cucugg), the phenotypic ratio will be 1:1:1:1. This means that there is an equal probability for the offspring to have curled ears and black fur, curled ears and gray fur, normal ears and black fur, or normal ears and gray fur. So, the final answers are: a.
In cats, curled ears result from an allele, Cu, that is dominant over an allele, cu, for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele, G, that is dominant over an allele for gray, g. A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F, cats are black and have curled ears.2. In cats, curled ears (Cu) result from an allele that is dominant over an allele for normal ears (c u). Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant over an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F t cats are black and have .In cats, curled ears result from an allele ( C u ) that is dominant to an allele (cu) for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele (G) that is dominant to an allele for gray (g). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F1 cats are black and have curled .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In cats, curled ears result from an allele (Cu) that is dominant over an allele (cu) for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele (B) that is dominant over an allele for gray (b). A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with .In cats, curled ears result from an allele, Cu, that is dominant over an allele, cu, for normal ears. Black color results from an independently assorting allele, G, that is dominant over an allele for gray, g. A gray cat homozygous for curled ears is mated with a homozygous black cat with normal ears. All the F_1 cats are black and have curled .
in cats curled ears result from an allele In cats, curled ears (Cu) results from an allele that is dominant overCell theory began to develop in 1839, following the research of Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann into plant and animal tissues. Both the botanist Schleiden and the physiologist Schwann noticed that every organism they viewed under a microscope, whether plant or animal, was composed of cells.
in cats curled ears result from an allele|In cats, curled ears (Cu) results from an allele that is dominant over
PH0 · Solved In cats, curled ears result from an allele, Cu,
PH1 · SOLVED:In cats, curled ears result from an allele (C u) that is
PH2 · SOLVED: In cats, curled ears result from an allele Cu, that
PH3 · SOLVED: In cats, curled ears result from an allele ( C u
PH4 · Patterns of allele frequency differences among domestic cat breeds
PH5 · Patterns of allele frequency differences among domestic cat
PH6 · In cats, curled ears (Cu) results from an allele that is dominant over
PH7 · Genetics Clicker Questions Exam 2 Flashcards
PH8 · Chapter 3 genetics Flashcards
PH9 · 7 Cat Ear Facts